The Cognitive Functions of Every Myers-Briggs® Personality Type
Today we’re diving into the cognitive functions of each Myers-Briggs (MBTI®) personality type. Want to find out how to harness the unique powers of your mind? If so, you’re in the right place!
Not sure what your personality type is? Take our in-depth personality questionnaire here. Or you can take the official MBTI® here.

Table of contents
- What are the cognitive functions?
- The Cognitive Functions of Each Myers-Briggs® Personality Type:
- The INTJ Cognitive Function Stack:
- The INFJ Cognitive Function Stack
- The INTP Cognitive Function Stack
- The INFP Cognitive Function Stack
- The ENTJ Cognitive Function Stack
- The ENFJ Cognitive Function Stack
- The ENTP Cognitive Function Stack
- The ENFP Cognitive Function Stack
- The ISTJ Cognitive Function Stack
- The ISFJ Cognitive Function Stack
- The ESTJ Cognitive Function Stack
- The ESFJ Cognitive Function Stack
- The ISTP Cognitive Function Stack
- The ISFP Cognitive Function Stack
- The ESTP Cognitive Function Stack
- The ESFP Cognitive Function Stack
- What Are Your Thoughts?
- References:
What are the cognitive functions?
Imagine a house with four rooms. You enter all the rooms at one point or another, but some rooms are more comfortable and familiar to you than others. These four rooms represent your cognitive functions – the ways in which you perceive information, make decisions, and interact with the world around you.
Each of us has a hierarchy of cognitive functions that we use on a daily basis. And just like we might spend more time in the bedroom or kitchen of our house, we might spend more time using one or two different functions.
Our cognitive function stack tells us what our hierarchy of functions is. For example, if you’re an ENTJ, your cognitive function stack would look like this:
An Example: The ENTJ Cognitive Functions
Dominant Function: Extraverted Thinking (Te)
Auxiliary Function: Introverted Intuition (Ni)
Tertiary Function: Extraverted Sensing (Se)
Inferior Function: Introverted Feeling (Fi)
These four functions are the “primary” functions of the ENTJ personality type. These are the functions that the ENTJ will associate with themselves; the functions that seem the easiest and most natural to use. The dominant function will be their “favorite room in the house”, while the inferior function might be the basement. It’s a room that they go into from time to time and they know they should feel comfortable there, but they can’t quite get rid of the feeling that it’s a little dark, a little less comfortable, and maybe a spider will crawl up their leg at any minute.
Beneath these four functions are what we call the shadow functions. For the ENTJ they would look like this:
An Example: The ENTJ Shadow Functions
Oppositional Role/5th function: Introverted Thinking (Ti)
Critical Parent/6th function: Extraverted Intuition (Ne)
Trickster/7th function: Introverted Sensing (Si)
Daemon/8th function: Extraverted Feeling (Fe)
The shadow functions are the functions we don’t associate with ourselves. We tend to project these functions onto others. They’re the parts of ourselves that we don’t realize we’re using, but that others may see, sometimes in negative or manipulative ways.
Today we’re going to focus on the primary functions. If you want to know more about the shadow functions I’ve written an article about that here: An Introduction to the Shadow Functions
The Cognitive Functions of Each Myers-Briggs® Personality Type:
The INTJ Cognitive Function Stack:
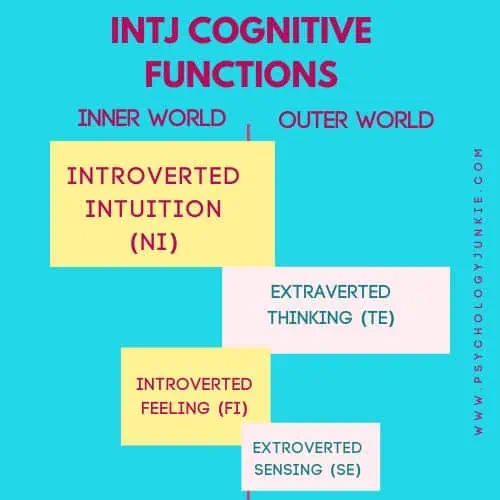
Dominant Function: Introverted Intuition (Ni)
Patterns, insights, concepts, ideas. This is the world of Introverted Intuition. This is the function that looks “behind the scenes” of reality; uncovering deeper meanings and trying to figure out the “why” behind it all. INTJs often get a sense of knowing that seems to appear out of the blue to others. When they can harness their focus on a particular future vision and then spot the ripple effects in the present moment that could lead to that vision they get a rush of energy and excitement. Ni is the tool that INTJs wield to anticipate how a situation will likely play out and work backwards from there in order to create the precise strategy. It’s also the function that gives INTJs a desire to understand the deeper meaning behind things. Why are we here? What’s the purpose of existence? What happens after we die? What do the symbols in our dreams signify? Questions like these seem like mental candy for the INTJ.
Thanks to Introverted Intuition, the abstract, rather than the concrete, will primarily be what energizes INTJs.
Auxiliary Function: Extraverted Thinking (Te)
Segmenting, organizing, delegating, solving. This is the world of Extraverted Thinking. This is the function that INTJs use to stay grounded in what’s provable, logical, and effective. Without a healthy connection to Extraverted Thinking, INTJs would be unrealistic and vague, lost in abstract musings and unable to bring their visions to fruition.
When INTJs tap into Extraverted Thinking they look at measurable facts, observable logic, and pass/fail metrics. They use Te to formulate effective strategies and easy-to-follow systems to achieve their goals. Many times they use Extraverted Thinking to support other people. If you come to an INTJ for help, chances are they’ll try to solve the problem, suggest strategies, or point out logical errors in your plan so that you can circumvent them.
Tertiary Function: Introverted Feeling (Fi)
Values, identity, beliefs, authenticity. This is the world of Introverted Feeling. This is the more vulnerable, childlike function of the INTJ personality type. While on the outside INTJs may seem stoic, tough, and immovable, on the inside they are more sensitive, idealistic, and principled. They have a sense of what matters to them as individuals, and they are not swayed by popular opinion. Their values are their own and they don’t need others’ approval in order to maintain them. Making sure they are in alignment with their values is crucial; and many times INTJs will go against the grain to stay true to themselves, showcasing an idiosyncratic quality that surprise others.
Because Introverted Feeling is tertiary for INTJs, they tend to be a bit guarded about how they feel. To express their feelings can put them in a place of vulnerability or childlike shame. They may also objectify their feelings in order to get a job done; silencing them much like a parent shushes a child who is getting in the way of an important task.
Inferior Function: Extraverted Sensing (Se)
Action, experience, details, reality. This is the world of Extraverted Sensing. This is the function that INTJs use to stay in touch with what’s really happening around them. Ultimately, Extraverted Sensing cares about what’s real and relevant rather than what’s beneath the surface. Because this function is inferior for INTJs, they can easily become overwhelmed by activity and sensory stimulation in the outer world. The tangible realities of life can feel suffocating, especially when the inner world of intuition seems so compelling and natural.
INTJs often have a strong desire to bring their ideas to reality; to see, feel, touch, and sense what they’ve created in their mind. But this requires getting out of their comfort zone and stepping into the energy of Extraverted Sensing. Some INTJs avoid this entirely while others gradually build up a relationship with this function.
During chronic or extreme stress, Se may become more pronounced in INTJs. They may become more easily provoked, impatient, restless, and controlling of the physical world. At times they may become hedonistic, overdoing it in unhealthy ways. Other INTJs over-exercise, or frantically clean, trying to feel more in charge of their bodies or their environments.
Find out more about INTJs: 10 Things People Misunderstand About INTJs
The INFJ Cognitive Function Stack
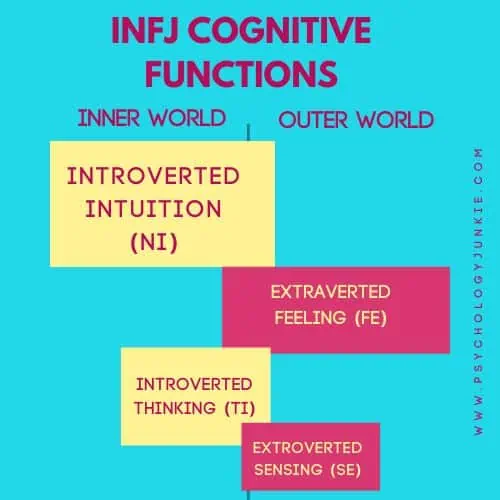
Dominant Function: Introverted Intuition (Ni)
The realm of patterns, insights, and abstract concepts is where Introverted Intuition thrives. INFJs, like their INTJ counterparts, frequently experience sudden insights that may seem out-of-the-blue to others. They have a knack for understanding the ‘why’ behind everything, exploring the depths of existence and symbolism. This function allows INFJs to envision the future and work backwards to devise a roadmap to their envisioned outcome. It also fuels their thirst for understanding life’s deeper meanings and existential questions.
Because INFJs have dominant Introverted Intuition, tapping into symbols, universal truths, and profound realizations is their modus operandi. It’s satisfying and energizing for them to be in a quiet, meditative place where they can focus on a particular vision, outcome, or idea. As much as possible they try to align themselves with this sense of peaceful knowing; and they may become agitated if they are in a hectic environment for too long without the opportunity to recharge.
Like INTJs, INFJs prefer the world of the abstract rather than the concrete. Focusing on concepts, ideas, and symbols will be more energizing for the INFJ than focusing on literal details and facts.
Auxiliary Function: Extraverted Feeling (Fe)
Harmony, empathy, and collective values characterize Extraverted Feeling. INFJs use this function to connect with others on an emotional level, understanding and often mirroring the feelings of those around them. It helps them create harmonious environments and promotes their desire for communal well-being. Without a solid connection to Extraverted Feeling, INFJs may feel detached, disoriented, and out of sync with the world and people around them.
Because Extraverted Feeling is in the auxiliary position for INFJs, they tend to use this function to support and help others. If you come to an INFJ with a problem, chances are they’ll try to empathize with you, validate your feelings, and see where you’re coming from emotionally. If you’ve ever wondered whether you’re an INTJ or an INFJ, you can see the difference here. An INTJ will try to solve the problem using logical means or by giving constructive advice; an INFJ is more apt to relate to someone, empathize verbally, and offer emotional support.
Tertiary Function: Introverted Thinking (Ti)
Analysis, precision, and internal logic define Introverted Thinking. This function has a more vulnerable quality to it for INFJs because of its placement in the tertiary position. While INFJs may seem warm, engaging, and sensitive on the outside, they can actually be quite analytical, precise, and skeptical on the inside. They just may not show this to others for fear of being incorrect in their assessments or being misinterpreted as unkind or insensitive.
INFJs are easily absorbed in theories, models, and frameworks and enjoy understanding how theoretical models work. Analyzing complex concepts and naming, defining, and organizing those concepts in their mind is often great fun for an INFJ. But they may avoid sharing their logical analysis with others unless they feel extremely comfortable.
Because Introverted Thinking is tertiary for INFJs, they enjoy receiving love and support in this area. They enjoy people who take their thoughts seriously; who can help them clarify the principles of their thinking and explain themselves with more clarity. People who are analytical and curious fascinate INFJs and help them bring their ideas into fruition with greater precision.
Inferior Function: Extraverted Sensing (Se)
Action, experience, reality, relevancy, and facts. These are the focuses of Extraverted Sensing, the function that INFJs utilize to stay connected with the present moment. Extraverted Sensing is all about acknowledging what’s tangible and relevant, rather than trying to figure out what’s going on beneath the surface. Because this function is inferior for INFJs, it tends to take a backseat. They can easily feel overwhelmed by noise, sights, sounds, tastes, and textures. The concrete realities of life may sometimes feel suffocating, particularly when compared to the compelling world of intuition.
INFJs have a strong desire to bring their ideas into reality, to see, feel, touch, and experience what they have imagined. But achieving this requires stepping out of their comfort zone and embracing the energy of Extraverted Sensing. Some INFJs will avoid this function as much as possible, while others gradually establish a relationship with this function over time.
During periods of chronic or extreme stress, Extraverted Sensing may become more prominent in INFJs. They may become easily agitated, impatient, restless, and seek out control over the physical world. At times, they may indulge in hedonistic behaviors or overcompensate through excessive exercise or frantic cleaning, attempting to regain a sense of control over their bodies or environments.
Discover more about INFJs: What Makes INFJs Dangerous
The INTP Cognitive Function Stack
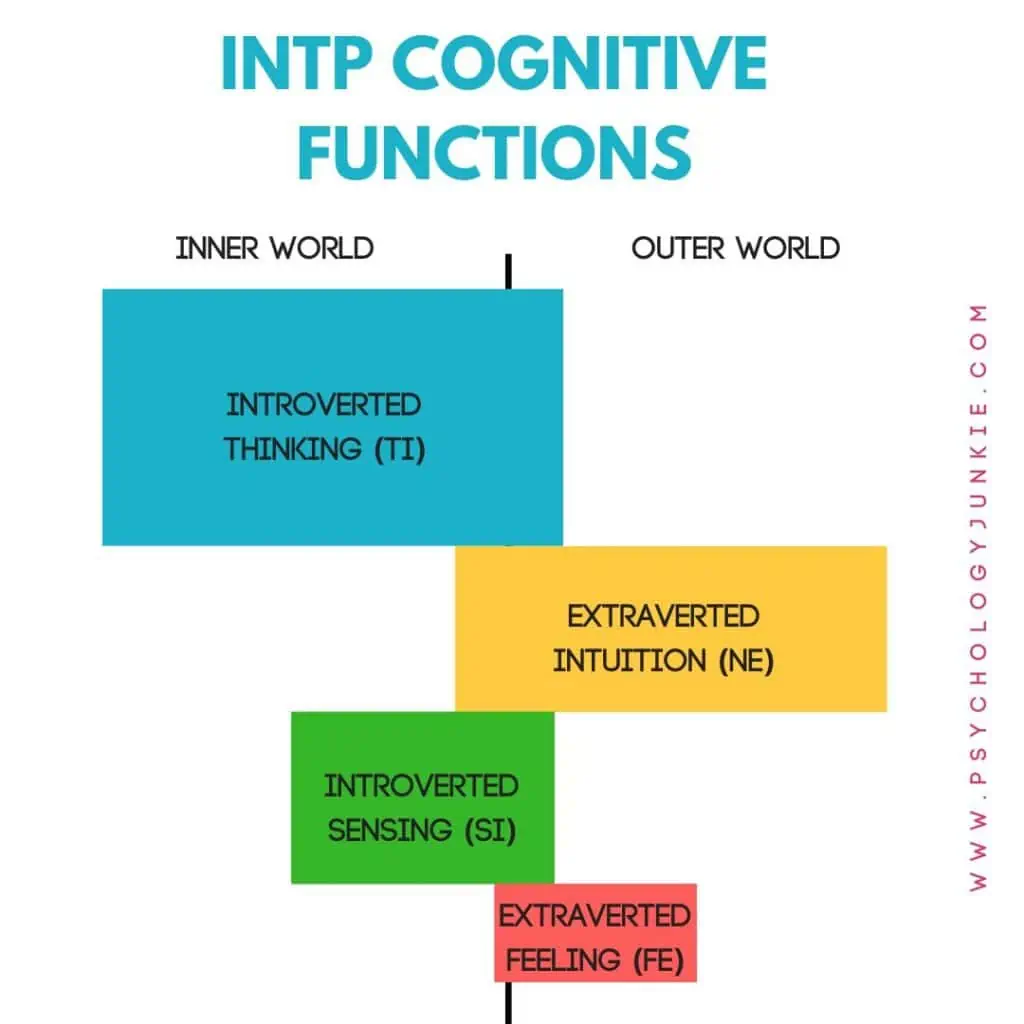
Dominant Function: Introverted Thinking (Ti)
Whenever you’re trying to figure out how something works down to its core components or principles, you’re using Introverted Thinking. This function, for INTPs, is all about detaching from situations in order to find various angles, principles, and leverage points. They love solving puzzles, analyzing and critiquing information to figure out what “doesn’t fit”, or experimenting to find what can be done to improve an existing system. INTPs get excited when they can figure out how an idea, theory, object, or concept works. Because of this they often enjoy arguing and debating, not to be oppositional or antagonistic but to learn more about a subject through thoroughly exploring its nuances and intricacies. As children, they are often found taking apart toys, putting them back together again, and then wondering what would happen if they added another piece or changed something else.
Auxiliary Function: Extraverted Intuition (Ne)
Extraverted Intuition is the INTP’s second most potent cognitive tool. It propels their curiosity and fuels their appetite for possibilities and novel ideas. With Ne, INTPs are adept at seeing alternative perspectives, brainstorming creative solutions, and making surprising connections between seemingly unrelated concepts.
Because Extraverted Intuition is in the auxiliary position for INTPs, they tend to use it in a way to support and help others. They have a gift for seeing possibilities others don’t and providing those possibilities and insights when someone is struggling. They can also help people to think outside the box and find creative or innovative solutions to problems.
Tertiary Function: Introverted Sensing (Si)
In the tertiary position, Introverted Sensing provides INTPs with a sense of familiarity and continuity. It allows them to recall past experiences, detail, and data, which can then be cross-referenced with their present situation. An INTP may use Si to remember a previously learned formula or to recall a past experience that offers insights into a current problem.
Because Introverted Sensing is in the tertiary position for INTPs, they tend to use it in a creative or playful way. Many INTPs enjoy movies, video games, or books they loved as children and will revisit them or geek out about them as adults. They may also use Si to reminisce over past experiences, stories, or memories that they find particularly interesting or enjoyable. That said, the tertiary function tends to feel a little vulnerable and INTPs can feel easily embarrassed if someone doesn’t honor their preferences here. However, they love it when people show an interest in their past experiences, their stories, or the familiar pastimes that bring them joy.
Inferior Function: Extraverted Feeling (Fe)
Extraverted Feeling, being the INTP’s inferior function, is often the most challenging for them to use. However, it provides a bridge to understanding others’ feelings and creating harmony. An INTP may have difficulty expressing their emotions or understanding others’ emotional needs. They prefer to focus on what makes sense; what’s logical, and how things work. Emotions can seem undependable and hazy to them; certainly not something to trust in decision-making. That said, INTPs still crave warm connections with others and appreciate feeling included and valued in group relationships. They just may not always be sure where they stand with a friend group, or they may feel hesitant to engage in small talk or social banter.
Stress and the Eruption of Extraverted Feeling in INTPs
Chronic or extreme stress can often trigger an eruption of Extraverted Feeling (Fe) in INTPs. When this happens, they don’t look like typical INTPs. Instead, they become unusually sensitive to external validation and social dynamics. “Do people like me?” “What impression am I making?” These questions will play more on their mind. An insatiable hunger for positive interactions or affirmation may emerge, and they might seek out validation and connection from others more than usual. They may fixate on how they are perceived, grappling with a sense of alienation and loneliness. This can lead to feelings of being misunderstood or undervalued during these times. However, in a positive sense, it can help INTPs to realize the importance of relationships, connection, and friendship.
Find out more about INTPs: The Unique Intelligence of INTPs, INFPs, ENTPs, and ENFPs
The INFP Cognitive Function Stack
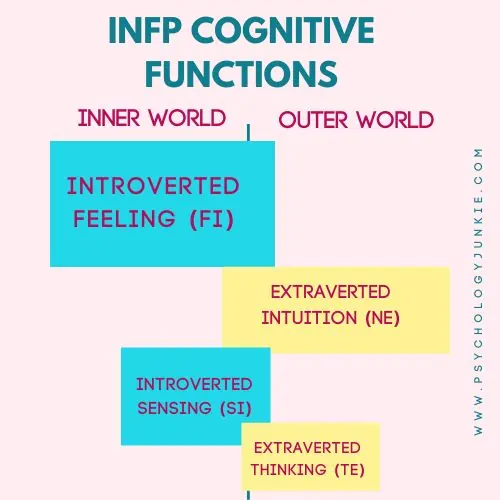
Dominant Function: Introverted Feeling (Fi)
Whenever you dive deep into your soul to figure out what matters to you on a core level; what matters to you regardless of what anyone else wants, you’re using Introverted Feeling. This is the INFP’s dominant function, and the mental tool responsible for making value-based judgments. For INFPs, the world is viewed in terms of how it lines up with their inner values and how they feel about what’s happening. They are passionate about advocating for their values and tend to experience emotions deeply. This intense emotional focus, however, often stays hidden from the external world. It can be a challenge for them to share their feelings, but when they do, it often comes out as creative expressions in the form of art, music, performance, or writing.
Auxiliary Function: Extraverted Intuition (Ne)
The second function for INFPs is Extraverted Intuition (Ne). This function allows them to see possibilities and potential everywhere. From a simple object or idea, they can generate a myriad of potential outcomes or solutions. They enjoy exploring abstract theories and concepts, and they can often surprise others with their innovative ideas. They use Ne to envision a better future, to think outside the box, get creative, and explore alternatives that others might never have dreamed of.
Because Extraverted Intuition is the auxiliary function for INFPs, they tend to use it in a supportive or nurturing way. This can look like dreaming up unique possibilities for someone, brainstorming with them, helping them to think outside the box, or nurturing their imagination.
Tertiary Function: Introverted Sensing (Si)
Introverted Sensing (Si) is the INFP’s tertiary function. This function is all about tuning into the past, in all its personal nuance, and using the memories to instill something significant or helpful into the present moment. When INFPs use Introverted Sensing they reminisce, recall age-old wisdom, or revel in routines and traditions that ground them.
Because Introverted Sensing is in the tertiary position for INFPs, they tend to have a playful, creative, childlike energy with it. They may enjoy commemorating their memories in creative ways; through poetry, scrapbooking, song, or art. They may also have special feel-good routines that comfort them during difficult moments. Receiving love and support in this area is crucial for INFPs. It means a lot to them when others value and honor their traditions or routines or take an interest in their stories or life experiences.
Inferior Function: Extraverted Thinking (Te)
Extraverted Thinking (Te) is the INFP’s inferior function. This function helps them organize their external world, make decisions based on logic, and construct efficient systems. Since it is their inferior function, they can feel a lot of uncertainty around it. They much prefer to focus on their values, what’s personally meaningful, or what their heart is driving them towards. Tapping into Extraverted Thinking can feel very cold and one-dimensional in contrast. However, they still value this function.
The struggle between valuing Extraverted Thinking and feeling uncertain around it can show up in many ways. INFPs often struggle to know the best logical decision to make and may get stuck in a place of indecision. Often they avoid giving criticism or struggle to make an effective plan of action that can be used to achieve their goals. However, with growth and practice, they can use this function to enhance their efficiency and make their dreams and ideals a reality.
Stress and the Eruption of Extraverted Thinking in INFPs
Under stress, INFPs might exhibit an uncharacteristic eruption of Extraverted Thinking. They might become overly critical and focused on efficiency, neglecting their usual concern for individual values and feelings. They might become fixated on getting their world in order and hyper-fixate on jobs that need to be done. In pursuit of a sense of efficiency they may become obsessed with their to-do list and get frustrated with people around them who all seem “incompetent” or “lazy.” This behavior is typically a stark contrast to their normal empathetic and easy-going nature.
Find out more about INFPs: Your INFP Personality and Your Enneagram Type
The ENTJ Cognitive Function Stack
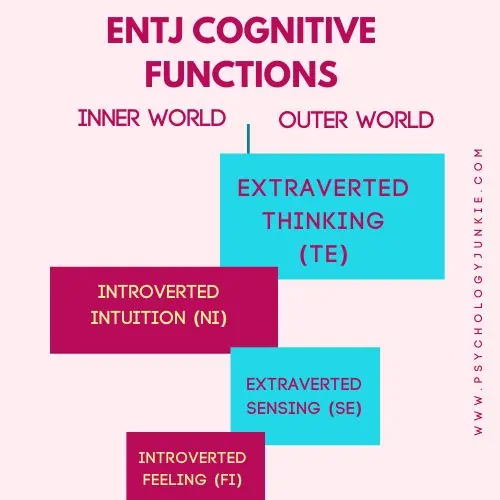
Dominant Function: Extraverted Thinking (Te)
Imagine the functionality of a well-oiled machine, every cog in its right place, operating smoothly to achieve a specific goal. This is an apt metaphor to describe the ENTJ’s dominant function, Extraverted Thinking (Te). This is the function you use when you have a goal and you create a sequential plan for making it a reality. Whenever you organize resources, analyze metrics, create contingency plans, or break things into workable elements, you’re using Extraverted Thinking. Because this is the dominant function of the ENTJ, they tend to trust it as their guide. Influencing others through reason, weight of facts and evidence, and giving logical explanations are all things that come naturally to them.
Auxiliary Function: Introverted Intuition (Ni)
The second function for ENTJs is Introverted Intuition (Ni). This function allows them to see patterns, connections, and future possibilities in what others may view as unrelated information. They can quickly synthesize large amounts of data into a single cohesive vision or prediction. Most ENTJs have a sense of certainty about what’s going to happen; an ability to see ripple-effects that others don’t. Rather than focusing on the present, they tend to fixate on what “will be”, creating a roadmap in their mind to follow to bring their ideas to fruition. At the same time, they have a desire to understand inner images, symbols, and epiphanies that seem to come to them out of nowhere. Because of this, many ENTJs have an interest in archetypes, metaphors, or philosophies about life.
Because Introverted Intuition is in the auxiliary position for ENTJs, they tend to use it in a supportive or nurturing way. This can look like giving someone insight into what’s going on for them, sharing a prediction that could help them avoid a problem, or giving them a sense of the deeper meaning of things. When ENTJs mentor others, they like to paint a picture of the potential they could reach or a goal they could achieve.
Tertiary Function: Extraverted Sensing (Se)
Extraverted Sensing (Se) is the tertiary function for ENTJs. This function immerses them in the present moment, allowing them to notice sensory details in their surroundings and react quickly to immediate realities. It’s the function that kicks in when you’re absorbed in a physical activity like rock climbing, or when you’re attentively appreciating the aesthetics of a gourmet dish or an intricate piece of art.
Because Se is in the tertiary position for ENTJs, it’s often used in a playful or recreational way. It’s also a way they enjoy receiving support and nurturing. This can show up like experimenting with cooking, dancing with a partner in a playful or silly way, or driving too fast when feeling vulnerable and anxious. Because this is also how ENTJ’s like to be nurtured and cared for, they can especially appreciate people who bring their awareness to the beauty of life, offer physical affection, or help them experience new sights, sounds, tastes, and feelings.
Inferior Function: Introverted Feeling (Fi)
Introverted Feeling (Fi) is the inferior function of ENTJs. This is the function that focuses on individual values; what someone feels and believes is right or wrong independent of what society says. When you get a gut feeling inside that something doesn’t sit right with you, you’re using Introverted Feeling. When you get a sense of satisfaction; that you’re on the right path and your conscience is at peace, you’re aligned with Introverted Feeling. This function encompasses a system of values, ethics, and emotions which are deeply personal and subjective. This function is activated when ENTJs reflect on their personal feelings and beliefs, or when they need to make a decision that aligns with their core values and principles.
Because this function is inferior for ENTJs, they might struggle with it, often neglecting their own feelings in favor of logical and pragmatic solutions. They may become out of touch with who they are, what they stand for, or what gives them a sense of alignment and peace. However, as they grow and develop, they can learn to incorporate this function better, learning to balance their drive for logical efficiency with a respect for individual values and emotional needs. This might manifest as standing up for a cause they believe in, giving money to a charity, or making time for leisure activities that help them feel calm or satisfied.
During times of extreme or prolonged stress, the inferior Introverted Feeling (Fi) of ENTJs can erupt, causing an uncharacteristic shift in their behavior and outlook. They may suddenly feel unappreciated, melancholic, or unloved, becoming unusually sensitive to any perceived unfair treatment. The normally goal-oriented and rational ENTJ may withdraw, ruminating on a deep-seated loneliness. This is often accompanied by a heightened awareness of personal desires and needs that had previously been overridden by their relentless focus on work and efficiency. These feelings are frequently intense and unfamiliar to the ENTJ, leading to a sense of disquiet and internal conflict.
Discover more about ENTJs: Understanding ENTJ Thinking
The ENFJ Cognitive Function Stack
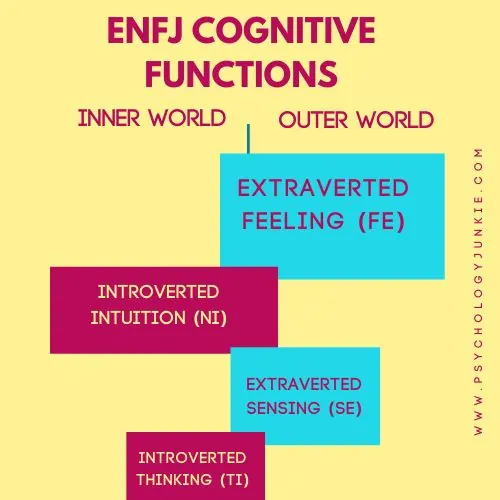
Dominant Function: Extraverted Feeling (Fe)
Do you ever just know how people are feeling and what emotional wavelengths are drifting through the atmosphere? Is it easy for you to alter your behavior to make sure everyone “gets along” and is comfortable? Do you notice the values that others ascribe to and try to honor them socially? When you do this, you’re using Extraverted Feeling. This cognitive tool empowers ENFJs to tune into the emotions of the group or environment around them, creating a strong sense of empathy and understanding. They are often described as ‘people persons’ due to their innate ability to foster harmony and handle group dynamics effectively.
To illustrate Fe in action, imagine a family gathering where tensions start to rise due to a disagreement between two members. An ENFJ, leveraging their dominant Fe, would intuitively sense the underlying emotional currents and work to diffuse the tension. They could help mediate the situation, expressing each person’s standpoint in a way that fosters understanding, and steer the conversation towards a resolution that maintains familial harmony. This ability to ‘feel into’ others and mediate conflicts is a core strength of Extraverted Feeling.
Auxiliary Function: Introverted Intuition (Ni)
Introverted Intuition (Ni), the auxiliary function of ENFJs, is like a deep-sea diver, plunging into the ocean of the subconscious and surfacing with pearls of insight. This function excels at seeing beneath the surface, spotting underlying patterns, and making connections that might not be immediately obvious. It thrives on abstract thinking, often using symbols or metaphors to encapsulate complex concepts.
To put it simply, imagine you’re watching a movie with an ENFJ. As the film unfolds, this friend might lean over and whisper, “Do you notice how the color blue shows up every time the main character has to make a decision? I think it symbolizes the feeling of being ‘at sea’ or ‘in the unknown’ that the character experiences at these moments.” That is Introverted Intuition at work! It’s like having a built-in radar that scans for deeper meanings and connections. This ability can make ENFJs insightful companions, capable of bringing fresh perspectives to light and encouraging others to think beyond the obvious.
Because ENFJs are Intuitives, the world of the abstract or conceptual will typically be more fascinating and energizing than the world of literal facts and details.
Tertiary Function: Extraverted Sensing (Se)
Extraverted Sensing (Se) is like a radar, highly attuned to the present moment, picking up on the finest details in the environment. It thrives on engaging with the world in a hands-on, tangible way, making ENFJs often aware of their surroundings and any changes occurring in them.
When an ENFJ uses their Extraverted Sensing, they might notice the new haircut of their colleague, the fresh smell of spring in the air, or the subtle change in the weather. They trust in the immediacy of the moment, often having an instinctual understanding of what’s happening around them and how it might influence the current context. They are astute in picking up what’s relevant now, and this ability can allow them to respond spontaneously and effectively to their surroundings.
As their tertiary function, ENFJs may not lean on this as heavily as their dominant and auxiliary functions, but when they do tap into it, it adds richness to their experiences. ENFJs also enjoy receiving support and love in this area. They appreciate people who can help them be more present in the moment by showing them the fun in the now and helping them seize the day!
Inferior Function: Introverted Thinking (Ti)
The ENFJ’s Inferior function is Introverted Thinking (Ti). This cognitive function is activated when ENFJs shift into a mode of introspection, systematically breaking down complex ideas to their essential parts. It enables them to understand and construct logical frameworks, verbalize precise definitions, and discover philosophical principles that are consistent and universally applicable. Whether it’s understanding the intricacies of a philosophical concept or diving deep into a specialized field of interest, Ti fuels the ENFJ’s intellectual curiosity and drive for analytical coherence.
To illustrate this, imagine an ENFJ engrossed in a book on theoretical physics. As they read, they don’t just skim over the concepts. Instead, they delve into the details, seeking to understand the underlying principles and equations that define the universe. They’re fascinated not just by the broad strokes but by the fine print, the precise definitions and logical structures that make up the grand scheme.
However, the use of Ti often comes into conflict with the ENFJ’s dominant function, Extraverted Feeling (Fe). ENFJs are primarily concerned with maintaining harmony and meeting others’ emotional needs. When personal issues arise, they may sideline their Ti-inclined introspection and analytical rigor, preferring to prioritize their natural ability to empathize and respond to others’ emotional needs.
During times of stress, the inferior function may manifest in unusual ways. The typically warm and empathetic ENFJ may become overly critical and analytical, fixating on minute details or inconsistencies that they would usually overlook. They may become engrossed in solitary intellectual pursuits, shunning their usual social engagement. This might look like an ENFJ suddenly spending hours poring over a philosophy book or obsessing over a single logical inconsistency in a conversation they had days ago. It’s a stark contrast to their usual behavior, and is usually a sign that they’re dealing with some pretty severe stress.
Find out more about ENFJs: What ENFJs Do When They Get Really Stressed Out
The ENTP Cognitive Function Stack
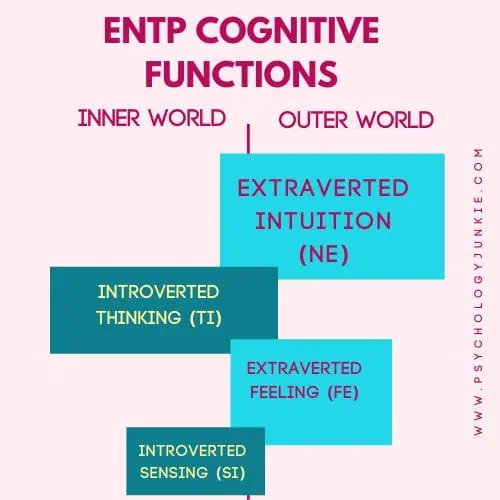
Dominant Function: Extraverted Intuition (Ne)
Do you ever have moments where possibility seems everywhere? Where one idea sparks a dozen more and suddenly you’re swimming in a world of potential and ‘what if’ scenarios?
Extraverted Intuition (Ne) is the function you’re using when this happens! As the dominant function of ENTPs, Ne allows them to perceive a multitude of possibilities in their environment. They’re excellent at spotting patterns and connections between seemingly unrelated concepts, making them innovative problem solvers. ENTPs are often seen as the “visionaries” of the personality types due to their ability to think outside the box and generate numerous innovative ideas.
Because Extraverted Intuition is the ENTP’s dominant function, they tend to believe that is it the best way to deal with any problem. So when life throws them hurdles; they’ll create a dozen more ways to get around it.
Auxiliary Function: Introverted Thinking (Ti)
ENTPs utilize Introverted Thinking (Ti) as their auxiliary function. This function helps them make sense of the world by applying logic and analysis. It’s all about understanding the underlying principles and structural workings of an idea or system. ENTPs strive for a deep understanding of the concepts that intrigue them and enjoy intellectual challenges. Their use of Ti contributes to their reputation as deep thinkers, able to dissect ideas and argue their points with precision.
Because Introverted Thinking (Ti) serves as the auxiliary function for ENTPs, they frequently use it to back and assist others. This shows up when they help others pursue clearer, more precise thinking and provide them with a more logical understanding of various components, particularly in troubleshooting scenarios. ENTPs are adept at clarifying complex concepts and untangling cognitive knots; their keen logical insights can illuminate the path towards clarity in principles. They act as intellectual liberators, removing the barriers of confusion and guiding others towards a coherent, rational comprehension of their thoughts and situations.
Tertiary Function: Extraverted Feeling (Fe)
Extraverted Feeling (Fe) is the tertiary function for ENTPs. This function is about connecting with others and understanding their needs and feelings. It’s less developed in ENTPs than Ne and Ti, but it still plays a significant role in how they interact with others. Given their natural tendency towards debate and argument, their Fe can help soften their approach, allowing them to consider the emotional impact of their words and actions on others. It also helps them to build harmonious relationships and influence the social dynamics around them.
Playfulness and Charm: The Tertiary Function of ENTPs
The Extraverted Feeling (Fe) function in ENTPs often manifests itself in a playful, childlike energy. They enjoy building a connection with others through playful charm, clever teasing, or provoking emotional reactions. This jovial nature is a unique aspect of their personality, which adds a light-hearted touch to their interactions. ENTPs also seek support and care in this function, appreciating affirmations, shared humor, compliments, and genuine connections. These positive reinforcements not only boost their morale but help them to feel genuinely cared for.
Inferior Function: Introverted Sensing (Si)
Introverted Sensing (Si) is the inferior function of ENTPs. This function is related to the awareness of inner bodily sensations and the ability to recall past experiences in detail. Because it’s their inferior function, ENTPs may struggle with routine, details, and the practical aspects of daily life. They much prefer the world of Extraverted Intuition, where they can deal with unknowns, explore new possibilities, and feel an ever-evolving sense of wonder about what they could create. In contrast, Introverted Sensing’s focus on details, stability, and the past can feel a little dull or even frustrating. However, there’s still a part of the ENTP that wants to be stronger in this area. Often as they age and mature, they work on developing their Si and become better at recalling facts and details while creating meaningful traditions and routines.
Stress and the Eruption of Introverted Sensing in ENTPs
When stressed, the ENTP’s inferior Si may trigger an over-focus on details, or a compulsive review of past events, often with a negative skew. They might become fixated on their mistakes and failures, replaying them over and over in their heads. They may also resist change, seeking comfort in familiar routines and traditions. This behavior is a stark contrast from their typical innovative and adaptable nature and is generally a sign that they’re extremely stressed and need a break.
Want to know more about ENTPs? 10 Things You Should Never Say to an ENTP
The ENFP Cognitive Function Stack
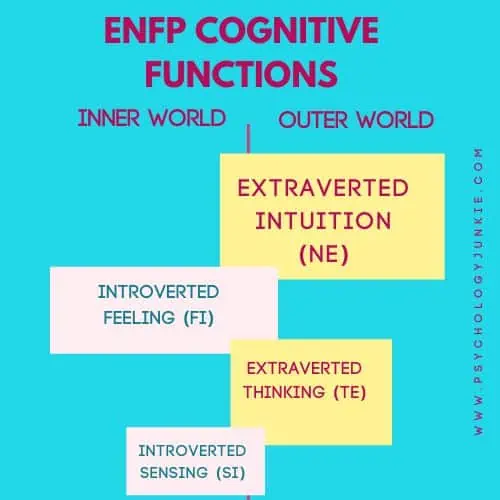
Dominant Function: Extraverted Intuition (Ne)
The dominant function of the ENFP is Extraverted Intuition (Ne). This function enables them to see the world through a lens of possibilities and potential. It’s like being able to see a multitude of future scenarios playing out simultaneously. ENFPs are experts at seeing connections between seemingly unrelated ideas or concepts, and they have a natural talent for brainstorming and ideation. They use Ne to generate creative solutions and innovative approaches to problems. This is why they are often known as the “inspirers” or the “campaigners” of the MBTI® types.
Because ENFPs are Intuitives, they are more energized by the world of ideas, concepts, and symbols than the world of literal details and facts.
Auxiliary Function: Introverted Feeling (Fi)
Introverted Feeling (Fi), for an ENFP, is about authentic self-expression. ENFPs use Fi to navigate their inner world and to understand and express their deeply held values, beliefs, and emotions. They are fiercely individualistic and value authenticity. More than what society dictates, ENFPs focus on what is right for them according to their own conscience. When making decisions, they often prioritize their personal values over impersonal analysis or societal expectations. They are driven to align their actions with what feels deeply right and true to them.
For the ENFP, Introverted Feeling (Fi) plays an integral role in how they interact with and support others. ENFPs, with their strong Fi, value individuality and authenticity highly, and they extend this to their relationships. They provide a safe, non-judgmental space for others to explore their true selves, encouraging them to honor their personal values, desires, and beliefs. They are often the ones cheering from the sidelines, encouraging you to pursue what genuinely resonates with you, even if it defies societal or conventional expectations.
Tertiary Function: Extraverted Thinking (Te)
Extraverted Thinking (Te) is the tertiary function for ENFPs. This function helps them to organize their outer world, make logical decisions, and get things done efficiently. When ENFPs engage with their Te, they become action-oriented, striving to execute their ideas and plans in the most effective manner. They may look more assertive and decisive, focusing on achieving objectives and measuring results.
ENFPs also appreciate support when it comes to Te-related decisions. They appreciate people who can give them constructive advice, help them organize their goals, or turn their broad visions into achievable milestones. They often need guidance in streamlining their myriad of ideas into a cohesive plan, learning to prioritize tasks, and maintaining a level of discipline to follow through. That said, ENFPs can feel more vulnerable with their tertiary function and can easily feel embarrassed when their plans fail to come to fruition or when they make an error with the logic of one of their decisions.
Inferior Function: Introverted Sensing (Si)
Introverted Sensing (Si) is the ENFP’s inferior function. This function allows them to recall the past, remember specifics, and apply past experiences to the present. Since it is their inferior function, they may struggle with routine and prefer novelty instead. Rather than learning from the past, they may barrel forward, focusing instead on generating new possibilities for the future. However, as they mature and develop their Si, they can learn to appreciate the value of tradition and routine, and become more adept at remembering details and facts.
Stress and the Eruption of Introverted Sensing in ENFPs
During extreme or chronic stress, the ENFP’s Si might erupt in unusual ways. They may become obsessive about details, control, and routine – behaviors that are typically alien to their normal spontaneous and open-ended nature. They might fixate on negative past experiences and fear repeating them. In their quest for structure, they may start imposing strict rules on themselves, striving for order and predictability in their lives. However, this is not their natural state, and it’s often a sign that they need a breather to re-calibrate. Getting alone, getting a change of scenery, or having a little time to organize their thoughts is very important when this happens.
Want to learn more about ENFPs? A Look at the ENFP Leader
The ISTJ Cognitive Function Stack
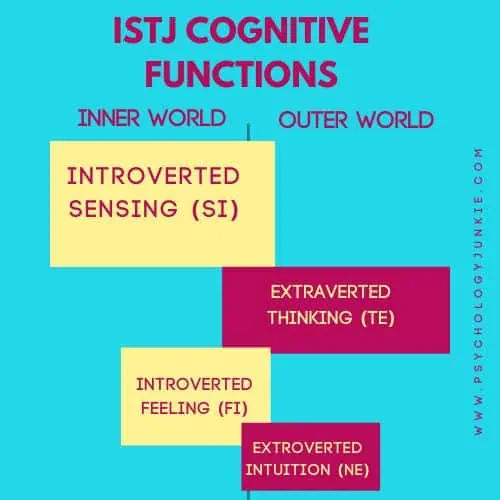
Dominant Function: Introverted Sensing (Si)
Stability. Routine. Tradition. Experience. This is the focus of Introverted Sensing. This function leads ISTJs to perceive the world through the lens of past experiences, giving them an exceptional ability to recall facts and details. They bring the wisdom of lived experience (and others’ lived experiences) to the table. This way they avoid “reinventing the wheel” and can provide practical, proven advice in situations that seem unsolvable. They value “how-to” knowledge and easily track where they are in a task and the sequence of how things should go. This function also gives them a fondness for traditions and routine, and they find comfort in repeating experiences that are meaningful to them. Their mind works to compare and contrast past to present, noticing changes, discrepancies, and meaning, and finding joy in the natural ebbs and flows and seasons of life.
Auxiliary Function: Extraverted Thinking (Te)
Structure. Goals. Organization. Objectivity. Efficiency. This is the world of Extraverted Thinking (Te). As the ISTJ’s auxiliary function, Te applies logic and structure to the external world. It is solution-oriented, time-conscious, and decisive. Te in ISTJs encourages their systematic approach to problem-solving and their penchant for clear rules and procedures. They are skilled at creating and maintaining order, ensuring everything runs like a well-oiled machine.
Because Te is in the auxiliary position for ISTJs, it is the primary way they show care and support for others. They use it to break down large tasks into manageable pieces or to provide practical, logical advice that is easy to implement. Their attention to detail and systematic approach often proves invaluable, especially in times of chaos or stress.
Tertiary Function: Introverted Feeling (Fi)
Introverted Feeling (Fi) is the tertiary function in ISTJs. Fi focuses on a set of internal values and beliefs, guiding ISTJs in determining right from wrong. Although ISTJs are often seen as outwardly stoic, the introverted feeling gives them a strong moral compass and a deep, if private, emotional world. It allows them to align their actions with their values, and gives them a desire to be authentic, real, and aligned with what really matters to them ethically.
Feeling Seen and Valued: The Desire of ISTJs through Introverted Feeling (Fi)
Because Introverted Feeling is the ISTJ’s tertiary function, it’s also the way in which they most appreciate love and support. They want to be recognized and appreciated for who they really are, not just for their achievements or efficiency. ISTJs deeply value their beliefs and principles and want to surround themselves with people who will honor that. And while they may not always openly express these values, that doesn’t make them any less important. Gently encouraging an ISTJ to voice their values can be encouraging, but remember, there’s no need to push too hard. They should feel comfortable, not pressured, in expressing their beliefs. This understanding, respect, and gentle encouragement can make an ISTJ feel seen, valued, and truly supported.
Inferior Function: Extraverted Intuition (Ne)
Extraverted Intuition (Ne) is the inferior function of the ISTJ. It helps them see possibilities in their environment and imagine what could be or how they could change things and innovate. As it’s their inferior function, ISTJs might initially struggle to embrace change or deal with uncertainty. They prefer to work with what’s proven, tried-and-true, and consistent. However, as they mature and develop their Ne, they can become more open to new ideas, and understand broader contexts, making them more adaptable to change.
Stress and the Eruption of Extraverted Intuition in ISTJs
When ISTJs are experiencing extreme or chronic stress, their inferior Ne might create a tendency to overthink or worry about all the things that could go wrong, leading to anxiety and pessimism. They might become more indecisive, second-guessing their decisions and feeling stuck in analysis paralysis. Suddenly the future is teeming with dark and negative possibilities and potentials. This is not typical of ISTJs who usually pride themselves on their decisiveness and practicality. While these “grip” experiences can be exhausting, they can also help ISTJs realize the importance of trying new things and changing up the possibilities and experiences of their lives.
Discover more about ISTJs: 21 Hobbies That ISTJs Love
The ISFJ Cognitive Function Stack

Dominant Function: Introverted Sensing (Si)
Memories. Traditions. Routines. Details. Experiences. This is the focus of Introverted Sensing (Si). As the ISFJ’s dominant function, Si draws upon the past, developing a keen understanding of historical contexts and learning from their own experiences.
Whenever you sink into a memory from the past and compare and contrast it with the present, you’re using Introverted Sensing. When you look at an object and recall it’s meaning in a distant memory and imbue it with a specific sentimental value, you’re using Introverted Sensing. Because this is the ISFJ’s dominant function, they hold a deep respect for proven methods and have a tendency to favor the familiar. They also have a sentimental side and a fondness for nostalgia and reminiscing. ISFJs remember details with remarkable accuracy, create a sense of continuity in life, and find comfort in consistency and regularity. It’s no surprise ISFJs are often seen as the keepers of information, especially when it comes to family histories and traditions.
Auxiliary Function: Extraverted Feeling (Fe)
Harmony. Empathy. Values. Connection. This is the world of Extraverted Feeling (Fe). As the auxiliary function, Fe helps ISFJs connect with others on an emotional level. When ISFJs are disconnected from their Feeling side, they are less conscious of others and can be more “stuck in a rut”. When connected to their auxiliary functions, ISFJs are empathetic, warm, nurturing, and aware.
This function is primarily concerned with harmony, social values, and the feelings of those around you. Being the ISFJ’s auxiliary function, Fe helps them to empathize with others, understand their emotions, and respond appropriately. This emotional intelligence makes ISFJs excellent at providing support and comfort. They are often the ones others turn to in times of emotional distress.
Tertiary Function: Introverted Thinking (Ti)
Introverted Thinking (Ti) helps ISFJs to analyze information and solve problems internally by weighing logic and looking for inconsistencies. Although not as dominant as Si or Fe, Ti equips ISFJs with the ability to think critically and make decisions based on logic and reason. When faced with difficult situations, Ti helps ISFJs to break down problems and find logical solutions.
Playfulness and Problem-Solving: The ISFJ’s Tertiary Use of Introverted Thinking (Ti)
As the tertiary function for ISFJs, Introverted Thinking (Ti) brings a childlike curiosity and enjoyment of problem-solving to the personality. ISFJs with developed Ti can often be found toying with brain-teasers, puzzles, and logical games, finding delight in the challenge and mental stimulation they provide. They also enjoy spending time with people who can dissect and analyze information with them, respecting their thoughts and ideas. Such mental explorations may seem playful, yet they serve a deeper purpose – they assist ISFJs in evaluating their beliefs, refining their understanding, and guiding their decision-making process.
Inferior Function: Extraverted Intuition (Ne)
Extraverted Intuition (Ne) is the inferior function in the ISFJ’s cognitive stack, and it’s often the source of some discomfort and uncertainty. Ne is all about exploring possibilities, making connections between ideas, and envisioning what could be. It’s about thinking outside the box, pushing boundaries, and reveling in change. While ISFJs long to explore their potential and to discover new creative possibilities, they can also feel overwhelmed by brainstorming, hypothetical scenarios, or dealing with unknowns. Instead, ISFJs prefer to lean towards the familiar and rely on their past experiences (Introverted Sensing) to navigate their present and future.
For ISFJs, Ne might initially manifest as a fear of the unknown or a reluctance to deviate from tried-and-true routines. However, as they mature and develop their Ne, they can become more comfortable with change and adapt more easily to new situations. ISFJs may find that embracing Ne allows them to broaden their perspectives and consider new possibilities, leading to try new things and experience more fulfillment in life as a result!
Stress and the Eruption of Extraverted Intuition in ISFJs
Under stressful conditions, an ISFJ’s inferior Ne might lead to an overwhelming sense of fear about what the future holds. They may overthink or worry excessively about the unknown, resulting in anxiety and restlessness. It may feel like their mind is generating dozens of negative possibilities all at once, and the ISFJ may feel trapped in a state of constant catastrophe as a result.
Find out more about ISFJs: 24 Signs That You’re an ISFJ, the Protector Personality Type
The ESTJ Cognitive Function Stack

Dominant Function: Extraverted Thinking (Te)
Objectivity. Evidence. Structure. Goals. Organization. These are the focuses of Extraverted Thinking (Te). As the ESTJ’s dominant function, this is the function that gives them their signature “can-do” attitude. Whatever situation arises, they’re pretty sure they can come up with a logical solution or plan to resolve it. ESTJs value results, focus on metrics, and are aware of time; organizing everything in their lives so that they can achieve maximum results without wasted effort. They excel at creating systems, managing resources, and upholding structures, making them natural leaders and effective administrators.
Auxiliary Function: Introverted Sensing (Si)
Experiences, memories, details, and routines are the focus of Introverted Sensing (Si). As the ESTJ’s auxiliary function, Si gives them a deep respect for facts, details, and past experiences. They draw upon their past experiences to make informed decisions in the present, rather than working with unknowns or untested systems. ESTJs value traditions and established methods, and they enjoy creating and maintaining routines. To them, the past isn’t just a blip on their timeline, but a rich story filled with meaning, wisdom, and lessons that they can apply to the present to create a sense of stability and purpose.
Because Si is the auxiliary function for ESTJs, they use it to help and support others. They may recall critical details from past experiences to guide others in similar situations. Their stability and dependability can be comforting and serve as a grounding force in an unpredictable environment. And their knack for creating and maintaining routines can be leveraged to help out friends who are more disorganized and unfocused.
Tertiary Function: Extraverted Intuition (Ne)
Extraverted Intuition (Ne) is the playful tertiary function for ESTJs, sparking their ability to see patterns and connections between ideas. It helps them spot future outcomes and explore new possibilities. While not as trusted by the ESTJ as Te or Si, when developed, Ne can add a touch of creative flair to the ESTJ’s practical and methodical approach.
Playfulness and Exploration: The ESTJ’s Tertiary Use of Extraverted Intuition (Ne)
The ESTJ’s tertiary function, Extraverted Intuition (Ne), can bring a sense of playfulness and exploration to their personality. Ne fuels their curiosity and opens their minds to a world of possibilities, encouraging them to toy with creative projects and novel ideas. It’s not unusual to find an ESTJ engrossed in a thought-provoking sci-fi movie or a captivating fantasy novel, dabbling in these exploratory genres as a means to stimulate their Ne. They might also apply the ‘what if’, innovative nature of Ne to hands-on hobbies like crafts, building, or cooking. This engagement with the imaginative and the unknown might seem a bit out of character for these typically pragmatic individuals, but it’s merely their Ne at play, providing a refreshing balance to their more grounded and methodical instincts.
Inferior Function: Introverted Feeling (Fi)
Introverted Feeling (Fi) is the ESTJ’s inferior function. It’s a function they value, but one they feel uncertain or insecure about. Fi is all about personal values, emotions, and authenticity. It’s about staying true to oneself and living in harmony with one’s inner values. For ESTJs, the world of logic and objectivity is always more trusted than the world of inner feelings and values. They may stand strongly for certain causes, but they may keep their own feelings and values very close to the chest. They may struggle to express their emotions and feel insecure when they get publicly emotional. Over time, as the ESTJ matures and develops their Fi, they become more in touch with their inner feelings and values, often gaining a deeper understanding of themselves and others.
Stress and the Eruption of Introverted Feeling in ESTJs
In times of extreme stress, the ESTJ’s inferior Fi might lead to emotional outbursts or hypersensitivity that is uncharacteristic of their normal behavior. They may pull away from people, isolating and becoming more consumed by their feelings. They may also feel overwhelmed by feelings and desires they’ve left on the backburner; feeling that they’ve been so busy trying to “get things done” that they lost themselves in the process. This “grip” stress reaction can be a catalyst for personal growth, as the ESTJ is forced to confront and address their suppressed emotions and values. It can lead to a newfound sense of self-awareness and a deeper understanding of their own needs and desires. It can also be negative, leading to a spiral of self-doubt and insecurity.
The ESFJ Cognitive Function Stack

Dominant Function: Extraverted Feeling (Fe)
Harmony, collaboration, empathy, and connection are the focuses of Extraverted Feeling (Fe). As the ESFJ’s dominant function, Fe is the driving force behind their outlook and behavior. They are naturally in tune with the feelings of those around them and strive to create harmony and positive interactions. ESFJs often have exceptional social skills, intuitively sensing the mood of a room and altering their behavior to either match or change the mood. Whenever you find yourself creating a “vibe” with someone, or using humor, self-disclosure, or personal warmth to create a social bond, you’re using Extraverted Feeling. This function is one that ESFJs are tapped into on a near-constant basis which is why they tend to excel at hosting, mentoring, and getting people to open up and feel included.
Auxiliary Function: Introverted Sensing (Si)
The ESFJ’s auxiliary function, Introverted Sensing (Si), gives them a deep appreciation for facts, details, and past experiences. They tend to draw from their rich memory bank to guide their decisions and actions in the present. They’re loyal to their traditions and to the wisdom they’ve gleaned from experience; and, as such, it can take a long time before they change their traditions or worldviews. They take pleasure in maintaining and creating routines, often serving as the glue that holds together families and social groups.
Service and Support: The ESFJ’s Use of Introverted Sensing (Si) in Assisting Others
Introverted Sensing (Si) plays an instrumental role in how ESFJs provide help and support to those around them. As their auxiliary function, ESFJs use Si as a tool of service, helping people out in practical and tangible ways. ESFJs, guided by their Si, are often the ones remembering important dates, meticulously planning events, or maintaining familial traditions that bring joy and cohesion to their loved ones. Their reliance on past experiences and details allows them to offer relevant and practical advice, and their love for routines can be used to bring order to situations that seem chaotic or disorganized.
Tertiary Function: Extraverted Intuition (Ne)
Extraverted Intuition (Ne) is the tertiary function of ESFJs, activating their ability to spot patterns, explore possibilities, and anticipate future outcomes. While not as trusted by the ESFJ as Fe or Si, when developed, Ne can infuse a layer of creativity and open-mindedness into the ESFJ’s pragmatic, detail-oriented approach.
Playfulness and Exploration: The ESFJ’s Tertiary Use of Extraverted Intuition (Ne)
The ESFJ’s tertiary function, Extraverted Intuition (Ne), introduces an element of playfulness and exploration to their personality. Ne triggers their curiosity and opens up a myriad of possibilities, inviting them to play with innovative projects and fresh ideas. It’s not unusual to find an ESFJ engrossed in a riveting mystery novel or a playful fantasy movie, using these mediums to tap into their Ne. They also may use Ne to explore creative avenues; using hand-me-downs or random objects to create something new and different. This fascination with the imaginative might seem slightly unusual for these typically down-to-earth individuals, but it’s simply their Ne at work, offering a vibrant contrast to their more grounded and past-focused tendencies.
Inferior Function: Introverted Thinking (Ti)
Introverted Thinking (Ti) is the ESFJ’s inferior function. It’s a function that they appreciate, but often feel unsure or uneasy about. Ti is all about internal logical structures, individual reasoning, and personal truth. It’s about breaking things down, understanding how they work, and making decisions based on an internal set of principles. For ESFJs, the world of interpersonal connections and external harmony is always more trusted than the world of detached analysis and internal logic. They may struggle to debate or question ideas, often preferring to rely on external consensus rather than a deep-dive of internal, detached analysis. With maturity and development, they may become more comfortable with their Ti, enabling them to balance their warm-hearted nature with increased critical thinking and objectivity.
Stress and the Eruption of Introverted Thinking in ESFJs
In times of intense stress, the ESFJ’s inferior Ti might erupt and cause them to appear different from their normal selves. They may isolate, become overly critical, and overanalyze their actions or those of others. They may start blaming themselves or others for their problems and become obsessed with finding “reasons” for this blame. This “grip” stress reaction can fuel personal growth, drawing their attention to the need for logical principles that are consistent. Conversely, it can also be negative, leading to a cycle of self-doubt, blame, and insecurity.
Find out more about ESFJs: 24 Signs That You’re an ESFJ, the Defender Personality Type
The ISTP Cognitive Function Stack
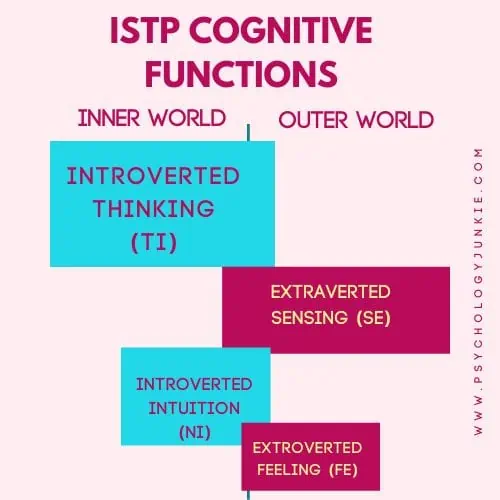
Dominant Function: Introverted Thinking (Ti)
Defining. Deducing. Categorizing. Analyzing. This is the world of Introverted Thinking. This function is focused on understanding how the world works. Because of this, ISTPs want to understand the nuts and bolts and principles of everything around them in order to create a personal framework of reality. Thanks to their constant probing into the “how” of everything, ISTPs are known for their problem-solving capabilities, breaking down complex situations into manageable components and capturing the essence of how things are built. They have a unique ability to shut out distractions and delve into their thoughts; separating the environment and body from the mind and getting into the roots of various arguments, theories, or problems that need solving.
Because ISTPs are Introverted Thinking dominant, the world of analysis and logical discovery will typically be more energizing than the world of emotional reflection and feelings.
Auxiliary Function: Extraverted Sensing (Se)
Extraverted Sensing (Se) serves as the ISTP’s auxiliary function, offering them a powerful, immediate connection to their surroundings. Se drives ISTPs to immerse themselves in the present moment, fully experiencing the physical world around them in vivid detail. It supports their Ti-driven problem-solving by providing a wealth of real-time, tangible data. This often shows up as a proclivity toward activities that require quick reactions and adaptability, such as sports, video games, or even emergency response careers.
Practical Engagement: The ISTP’s Use of Extraverted Sensing (Se) in Solving Problems
When tackling problems, ISTPs use their Extraverted Sensing (Se) to engage with the task at hand in a hands-on, practical manner. This is also the function that ISTPs use to support and care for others; they intuitively understand the physical needs or material requirements of those around them and are quick to offer solutions. They also enjoy showing others a good experience that gets them in touch with the present moment and the sensory details around them.
Tertiary Function: Introverted Intuition (Ni)
The ISTP’s tertiary function is Introverted Intuition (Ni). Although not as trusted by the ISTP as Ti, Ni offers an ability to perceive underlying patterns and predict possible outcomes. This function, when developed, can provide a strategic edge to the ISTP’s problem-solving, enabling them to foresee potential obstacles and plan accordingly.
Insight and Strategy: The ISTP’s Tertiary Use of Introverted Intuition (Ni)
ISTPs leverage their Introverted Intuition (Ni) to bring a layer of deeper insight to their practical problem-solving. While they are typically grounded in the present, their Ni allows them to anticipate future obstacles and potential outcomes. This is also the function that ISTP’s want to be shown care and consideration with. They are often drawn to people who can provide insight, explore concepts with them, or listen to their intuitive thoughts and abstract theories.
Inferior Function: Extraverted Feeling (Fe)
Extraverted Feeling (Fe) is the function that ISTPs feel the most uncertainty around. It’s responsible for understanding and responding to the emotions of others, aiming to create harmony and rapport. Because this function is inferior for ISTPs, they can sometimes come off as detached or indifferent to the feelings of others. They much prefer to work with the world of logic; where everything can be understood rationally. The world of feelings can seem cloudy, vague, and undependable to them. However, as they grow and develop, they may come to appreciate the value of emotional connections and see more clearly how to empathize with others.
Stress and the Eruption of Extraverted Feeling in ISTPs
Under extreme stress, ISTPs may show an uncharacteristic display of emotional behavior driven by their inferior Extraverted Feeling (Fe). This can result in sudden outbursts of emotion or a hypersensitivity to the feelings and opinions of those around them. This unusual behavior can act as a catalyst for personal growth, pushing the generally logical and reserved ISTP to explore their emotional side and develop a deeper connection with others. However, it can also lead to heightened anxiety and self-doubt if not understood and managed appropriately.
Find out more about ISTPs: The ISTP – An In-Depth Look
The ISFP Cognitive Function Stack

Dominant Function: Introverted Feeling (Fi)
Valuing. Listening. Aligning. Feeling. Harmonizing. This is the world of Introverted Feeling. As the ISFP’s dominant function, Introverted Feeling gives them a heightened awareness of what feels right or wrong to them. More than focusing on others’ values, ISFPs focus on their inner value system and must define for themselves what their conscience is telling them to do. Their life is a continual process of discovering what matters to them on a deep and fundamental level and tailoring their life around those values. For some ISFPs, the values could be a particular cause that’s close to their heart. For others, it could be creative expression or familial loyalty. More than anything, ISFPs strive to be true to themselves and create space for others to be their real selves as well.
Auxiliary Function: Extraverted Sensing (Se)
The ISFP’s auxiliary function, Extraverted Sensing (Se), gives them a vivid awareness of their immediate environment. This function compels them to immerse themselves fully in the present moment, experiencing and appreciating the sensory details of their surroundings. This can translate into an affinity for artistic or sensory-rich activities, such as visual arts, music, or nature.
Sensory Engagement: The ISFP’s Use of Extraverted Sensing (Se) in Interacting with the World
ISFPs use their Extraverted Sensing (Se) to interact with the world around them in a tangible, immediate way. They are keen observers, adept at noticing small changes in their environment or in people. They also use Se to support and care for others; this can show up in the way they try to bring positive experiences to people or use creative expression to connect with others in a tangible way.
Tertiary Function: Introverted Intuition (Ni)
Introverted Intuition (Ni) serves as the ISFP’s tertiary function. Though not as prominent as Fi, Ni presents itself as a quiet, internal voice that can perceive patterns, form insights, and anticipate future possibilities. This function often provides a springboard for their creative endeavors, helping them translate abstract ideas into tangible, aesthetic expressions.
Insight and Forecast: The ISFP’s Tertiary Use of Introverted Intuition (Ni)
ISFPs use their Introverted Intuition (Ni) to add a degree of depth to their observations and creations. They may not always be conscious of its influence, but their Ni often guides them towards a deeper understanding of the world around them. ISFPs also want to receive care and support in this realm. This means they are drawn to people who have rich insights, a curiosity about concepts, and a drive for meaning and understanding of the bigger picture. They also appreciate when people listen to their insights and respect the patterns and theories they’ve discovered.
Inferior Function: Extraverted Thinking (Te)
Extraverted Thinking (Te) is the ISFP’s inferior function and it focuses on logical analysis, efficiency, and productivity. Because it’s their inferior function, ISFPs may struggle with organizing their external world, making objective decisions, and expressing their thoughts bluntly and systematically. Instead, they much prefer the world of Introverted Feeling, where they trust their conscience and values to guide them. However, with personal growth and maturity, they can develop Extraverted Thinking further and use it to bring more structure and balance to their decisions.
Stress and the Eruption of Extraverted Thinking in ISFPs
In times of extreme stress, ISFPs may exhibit behaviors influenced by their underdeveloped Extraverted Thinking (Te). This could manifest as a sudden insistence on logical order, an uncharacteristic focus on efficiency, or a tendency to criticize others’ lack of organization or logic. While these behaviors can be unsettling for the typically easy-going ISFP, they can also spur personal growth by highlighting the importance of balance between their emotional and logical sides. However, if not understood and managed appropriately, these stress reactions could spiral into frustration and rash decisions they inevitably regret later.
Discover more about ISFPs: 24 Signs That You’re an ISFP, the Virtuoso Personality Type
The ESTP Cognitive Function Stack
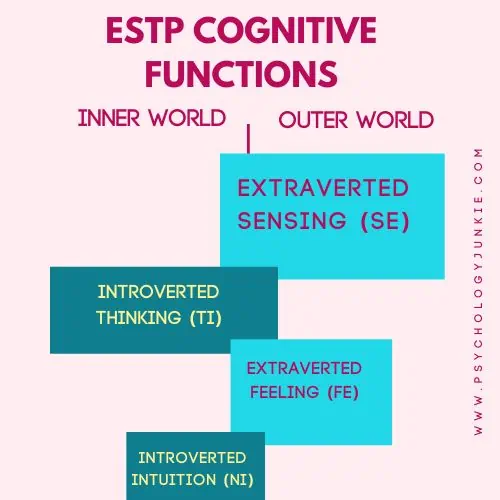
Dominant Function: Extraverted Sensing (Se)
Action. Immersion. Relevance. Details. Opportunities. Experience. These are the words we often associate with Extraverted Sensing. This cognitive function equips ESTPs with a keen awareness of their immediate surroundings and a remarkable ability to respond swiftly to changes in their environment. It helps ESTPs to live in the moment, engage in sensory-rich experiences, and spot opportunities. They are often drawn to thrilling, real-world adventures that allow them to exercise their spontaneous and pragmatic nature.
Extraverted Sensing is also focused on relevance. You’re unlikely to ever meet an ESTP with their “heads in the clouds. Rather, ESTPs pay attention to what matters in the moment. They’re always looking for opportunities, spotting details, and responding quickly if a crisis occurs.
Auxiliary Function: Introverted Thinking (Ti)
The secondary function of ESTPs, Introverted Thinking (Ti), helps them to make sense of the world by analyzing, categorizing, and understanding their experiences in a logical way. This function supports their decision-making process, enabling them to dissect problems and figure out the principles behind various arguments, theories, or issues. It also fuels their curiosity, driving them to dig deeper and understand the inner workings of things. Young ESTPs are often chastised for taking things apart to see how they work, and as adults they often spend a good deal of their time repairing or building things.
Logical Analysis: The ESTP’s Use of Introverted Thinking (Ti) in Decision Making
ESTPs use their Introverted Thinking (Ti) to break down complex situations into simpler, manageable parts. This is also the function they use to care for and support others. They do this by troubleshooting, offering logical input, or helping people to find clarity when their thoughts are muddled or confused. It can also look like arguing, but with good intent. ESTPs believe that giving truth is a form of giving love. If they can help someone spot inconsistencies in their thinking and give them a “cleaner” logic, they feel they’ve been able to help out.
Tertiary Function: Extraverted Feeling (Fe)
Extraverted Feeling (Fe) serves as the ESTP’s tertiary function. It influences their understanding and management of social dynamics and interpersonal relationships. While it doesn’t come as naturally to ESTPs as Se or Ti, they can leverage this function to be more aware of others’ emotions and to create harmony in their social interactions. Many ESTPs have a certain charm and playfulness that is thanks to their use of Fe. They have a way of knowing when to add levity or humor to a situation in order to diffuse tension or create a bond.
Interpersonal Harmony: The ESTP’s Tertiary Use of Extraverted Feeling (Fe)
Because Extraverted Feeling is the ESTP’s tertiary function, they tend to want love and support in this area. They may not outright admit it, but they love compliments, affirmations, and warm, positive interactions. Getting into a positive “vibe” with someone and creating rapport gives them a thrill; and they feel especially happy when others seem happy to be with them.
Inferior Function: Introverted Intuition (Ni)
Introverted Intuition (Ni) is the function that ESTP’s tend to feel the most uncertainty around. This function, which focuses on internal insights, future predictions, and abstract concepts, is often underdeveloped in ESTPs. They may struggle with long-term planning and may overlook potential future consequences of their actions. Instead, they prefer the world of Extraverted Sensing, where facts, reality, and real experience are the basis for understanding. However, as they grow and mature, they may start to tap into this function more, enhancing their strategic skills and ability to anticipate future outcomes.
Stress and the Eruption of Introverted Intuition in ESTPs
Under immense stress, ESTPs may experience an eruption of their underdeveloped Introverted Intuition (Ni). This can result in an unusual focus on negative future outcomes or an obsession with hidden meanings. While this can be disconcerting for the typically present-focused ESTP, it can also spark personal growth by encouraging them to consider future implications and develop a deeper awareness of abstract concepts. However, if not managed properly, this stress response can lead to anxiety and feelings of being overwhelmed.
Want to know more about ESTPs? 24 Signs That You’re an ESTP, the Daredevil Personality Type
The ESFP Cognitive Function Stack

Dominant Function: Extraverted Sensing (Se)
Experience. Enjoyment. Action. Aesthetics. Options. Impulses. These are words we often associate with Extraverted Sensing. As the ESFP’s dominant function, Se gives them an acute awareness of the physical environment and a drive to fully experience the sensory pleasures of the world. This cognitive function propels ESFPs to be spontaneous, action-oriented, and engaged with the world around them, often leading them to seek thrilling and exhilirating experiences.
Extraverted Sensing is also focused on what’s relevant and real. ESFPs (and ESTPs) are often called the “ultimate realists” because they have such a practical, present focus. Rather than getting distracted by hypothetical possibilities or premonitions, they focus on what actually happened, real details, and facts. Because of this, ESFPs (and ESTPs) have an extremely down-to-earth, unruffled demeanor and a highly pragmatic view of life.
Auxiliary Function: Introverted Feeling (Fi)
The secondary function of ESFPs, Introverted Feeling (Fi), provides them with a strong internal compass of values and emotions. This function supports their decision-making by focusing on authenticity and aligning actions with their deeply held values. For ESFPs, being true to themselves and authentic is far more important than fitting in or subscribing to social norms and commonly-held values.
Compassionate Advocacy: The ESFP’s Auxiliary Use of Introverted Feeling (Fi) in Supporting Others
ESFPs use their auxiliary Introverted Feeling (Fi) function to give care and support to others. In their drive to create an environment where individuals feel safe to express their authentic selves, they often emerge as advocates for those who struggle to make their values heard. It’s not uncommon for ESFPs to champion the underdogs, providing them with the support and encouragement they need to assert their individuality.
Tertiary Function: Extraverted Thinking (Te)
Extraverted Thinking (Te) is the ESFP’s tertiary function. While not their most natural strength, it helps them organize their external world, implement plans, and work efficiently towards their goals. As they mature, they often become better at using this function to bring structure to their ideas and actions.
Efficient Actions: The ESFP’s Tertiary Use of Extraverted Thinking (Te)
Because Extraverted Thinking (Te) is the ESFP’s tertiary function, it plays a significant role in how they receive love and support. ESFPs love people who take the time to listen to their plans, engage in strategic discussions, and offer assistance in developing practical roadmaps to achieve their goals. This collaborative approach makes ESFPs feel valued, understood, and supported, promoting a sense of deep emotional connection and happiness.
Inferior Function: Introverted Intuition (Ni)
Introverted Intuition (Ni) is the function that ESFPs feel the most uncertainty around. This function, which is concerned with future planning, abstract concepts, and internal insights, is often underdeveloped in ESFPs. They may have difficulty envisioning the future and understanding complex theories. Instead, they prefer the world of Extraverted Sensing, where things just “make sense” and life is understood through real experience and real facts. However, with personal growth, ESFPs can strengthen this function to better anticipate future events and make deeper connections between ideas.
Stress and the Eruption of Introverted Intuition in ESFPs
Under extreme or chronic stress, ESFPs may experience an eruption of their underdeveloped Introverted Intuition (Ni). This can result in uncharacteristic overthinking, fixation on future uncertainties, or dwelling on abstract problems. While this can be unsettling for the typically practical and present-focused ESFP, it can also stimulate personal growth by pushing them to consider long-term implications and delve into abstract thinking. However, if not managed effectively, this stress response can lead to anxiety and a feeling of being lost or overwhelmed by gloomy premonitions.
Want to know more about ESFPs? What It Means to be an ESFP Personality Type
What Are Your Thoughts?
We hope this exploration of cognitive function stacks has provided you with some valuable insights. Understanding your personality type and the way you process information can be a powerful tool for personal development. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions in the comments section below! We’d love to hear from you!
Tap into even more discoveries of your personality type in our eBooks, Discovering You: Unlocking the Power of Personality Type, The INFJ – Understanding the Mystic, The INTJ – Understanding the Strategist, and The INFP – Understanding the Dreamer. You can also connect with me via Facebook, Instagram, or Twitter!
References:
Building Blocks of Personality Type by Leona Haas and Mark Hunziker (2006, Eltanin Publishing)
Understanding Yourself and Others® An Introduction to the Personality Type Code by Linda V. Berens and Dario Nardi (InterStrength, 2004)









Informative article. I like that you said that the dom, aux, tert, & inferior functions are the top four. I was previously confused about this and wondered if the inferior was supposed to be the type’s very last function (#8) or #4. For me, SE is my #8. I’m like Ni when it comes to diving deep and exploring the why, but not when it comes to ideas just popping out of nowhere. I don’t have psychic ability and can’t predict the future without knowing how. Ni is often described as like a psychic knowing. For me, I can predict outcomes based on the input (cause and effect, based on history and past experience), which sounds like a sensing function. But S types are supposed to be traditional, and I’m not. INTJ describes me very well for the most part.
I like that you wrote “If you’ve ever wondered whether you’re an INTJ or an INFJ, you can see the difference here. An INTJ will try to solve the problem using logical means or by giving constructive advice; an INFJ is more apt to relate to someone, empathize verbally, and offer emotional support.” I’m definitely more like INTJ here. However, in the descriptions of the two types, I’m more like INFJ in the area of interest that they have; INTJs are more interested in math and science while INFJs are more interested in fiction and psychology. I’ve gotten INTJ as my result on tests more often, but I used to find it inaccurate because of how robotic the descriptions would make INTJ sound. I’m full of emotion; I just keep it inside. I guess I’d summarize it as: I’m emotional with myself but logical with others. I guess this could be the Fi and Te functions, which would be consistent with the function stack theory. But then with strangers, I put on a mask of kind politeness, which I guess is Fe, and then I wonder if I’m more like INFJ again….
My enneagram type is 4 (5 wing), and it’s usually F types that are type 4. I’ve always been in tune with my emotions and good at reading people, while my logical side didn’t come about until I got older. On enneagram tests, I’d usually get 5 as my result, but 4’s description seemed more accurate of me (feeling unique, misunderstood, creative, emotional, ashamed, and writing autobiographical stories).
Something I still need the answer to is how Myers and Briggs arrived at their conclusion that each type had this particular function stack in this particular order. I’m not convinced that Ni should be dom in INTJ. Why not Ti? Ni is often described as spontaneous too, which is like P, so I think Ni as dom would fit better for an INTP or INFP. Did Myers and Briggs just go with whatever dom function they felt like assigning to each type (that happened to be one of the letters in the 4 letter type), or is there actual science to back up their opinions? Did they survey people to ascertain their function stacks? My top three are Fi, Ti, and Si, which the theory says is impossible.
This article is incredible! It’s so in-depth, explains the functions remarkably well and helps me to understand how my husband thinks and why he reacts the way he does. It also explains how I can seem to others a warm, helpful, presence while inside I feel very calculating – not in a bad way, but in a “figuring out this situation so I survive it” way.
In short, it’s a triumph!
Great article, very informative. Just one question: when under stress, I use to get angry faster. Already when healthy, short-temperedness is one of my main weaknesses. Can this be ascribed to inferior Fi as well or to a higher degree to weaker Se (like childish, immature us of it)? Greetings from an ENTJ 784.
Hi. INFJ type here. I know it’s been a couple of months, but I wanted to respond to a couple of things you wrote to clear up confusion about your type. Ni isn’t a psychic feeling. It’s more like you know the answer then you need to work backwards to work out what brought you to the conclusion. You see the cause and effect, you just see the answer first. From the outside this can look mystical but it’s not. Also, being into STEM subjects is an INTJ stereotype. They’re not all like that. Men and women often have different interests to each other as well. I hope this helps.